What is Trauma?
Why Trauma?
Traumatic injury is the leading cause of death in Americans under the age of 45 and the fourth leading cause of death overall for all ages. Despite this chilling statistic, trauma research has historically been underfunded by the US federal government relative to its impact and cost on society. As a result, innovation in trauma care has failed to keep pace with other health conditions.
What do we mean by trauma?
CARIT is concerned with advocating to enable innovation in physical trauma care, as opposed to psychological or other types of trauma by representing multi-disciplinary membership.
Physical trauma refers to physical injury. In medicine, however, the words trauma patient usually refers to someone who has suffered serious and life-threatening physical injury potentially resulting in secondary complications.
The two main types of physical trauma are:
- Blunt force trauma—Caused by an object or force striking the body, often causing concussions, deep cuts, or broken bones. 1
- Penetrating trauma—Caused by an object piercing the skin or body, usually creating an open wound.
The National Academy of Sciences published a report in 2016 that cites specific unmet needs within trauma care to be addressed in order to save lives and highlights the need for a joint military and civilian approach to trauma care.2
Although surgical professional societies and others have advocated for change, we seek to mobilize the broader communities of stakeholders in trauma care and research to advocate for action as a unified front. Broad-based advocacy will enable trauma-care research to obtain the resources necessary to make rapid advances and to take advantage of foundational science in related fields.
Trauma Statistics and Facts
- 214,000 people die from traumatic injury each year — 1 person every 3 minutes.3
- In 2015 alone, 2.8 million people were hospitalized due to traumatic injuries and 27.6 million people were treated in an emergency department3
- Economic impact: In 2013, the cost of traumatic injury in the United States was $671 billion and the average cost per patient per year is $75,2104
- Only 3.7% of all NIH grants administered in 2016 were to fund trauma research5
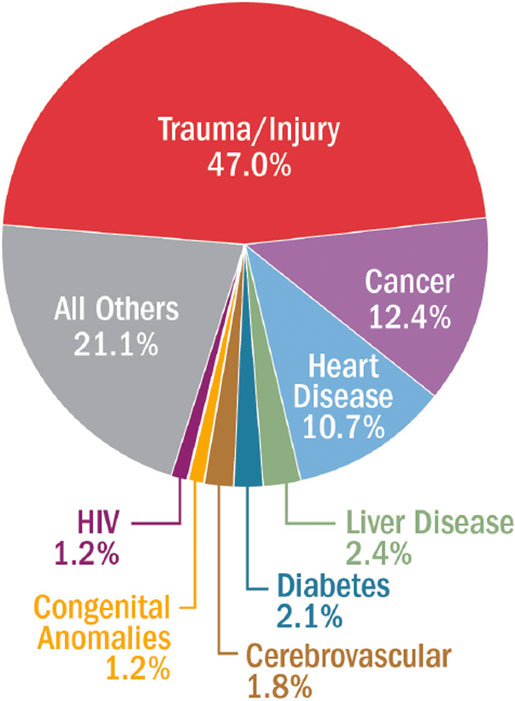
Leading Causes of Death, United States, 2014, Ages 1-46 years
SOURCE: Data from the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
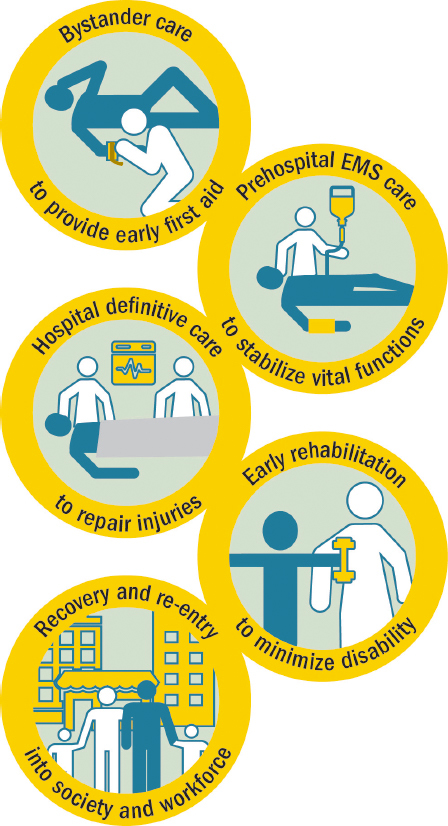
Trauma Care Chain of Survival
SOURCE: National Academy of Sciences 2016 Report in Brief
1 National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS, 2018)
2 Committee on Military Trauma Care’s Learning Health System, A National Trauma Care System: Integrating Military and Civilian Trauma Systems to Achieve Zero Preventable Deaths After Injury. National Academies Press (US) (2016)
3 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, 2017)
4 Weir, S. et al. One-year treatment costs of trauma care in the USA. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 10, 187–197 (2010)
5 Glass, N. E., Riccardi, J., Farber, N. I., Bonne, S. L. & Livingston, D. H. Disproportionally low funding for trauma research by the National Institutes of Health: A call for a National Institute of Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 88, (2020).
